6 Tips for Managing Your High Blood Pressure
February is American Heart Month and is aimed at encouraging Americans to focus on their heart health. According to the CDC, heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States and more than 18 million people have it. One of the leading causes of heart disease is high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. High blood pressure is where the force of the blood through your blood vessels is too hard which over time can lead to damage to your blood vessels. Uncontrolled high blood pressure occurs when you don’t know you have high blood pressure or don’t have it under control. This can put you at greater risk for stroke, vision loss, heart failure, heart attack, sexual dysfunction, and kidney failure. The best way to prevent having uncontrolled high blood pressure is by having regular visits with your doctor or advanced practice provider* (APP). They will work with you to determine what your blood pressure reading should be, which medications to take, and what if any lifestyle changes you should make. Here are 6 tips to help you manage your high blood pressure.
Be aware of over-the-counter (OTC) medications.
An important and easy lifestlye change you can make to manage your high blood pressure is learning which OTC medications can raise your blood pressure directly or have interactions with your blood pressure medications. Here is a guide you can use to discuss OTC medications with your doctor, APP, or pharmacist before taking them.
- Cold and cough medications. Many cold and cough medications contain a decongestant, such as pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine, which can raise your blood pressure.
- Energy supplements. OTC medications that make claims to help with your energy levels often contain caffeine or guarana. These ingredients can directly raise your blood pressure. If you have high blood pressure, it is recommended to consume less than 200 mg per day of caffeine.
- Pain, headache, and migraine medications. Certain OTC pain medications, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can raise blood pressure, especially in patients with kidney disease. These pain medications can also interact with blood thinners. Please check with your doctor, APP, or pharmacist about which OTC pain medications are safest for you.
- Weight loss medications. OTC medications for weight loss have similar ingredients to energy supplements. They attempt to reduce your appetite through stimulants and herbal ingredients, and can raise your blood pressure and interact with your other medications.
- Herbal medications. There are supplements and herbal medications that can be considered for patients with high blood pressure, but there are others that can raise blood pressure. Some of the herbal ingredients shown to increase blood pressure include arnica, bitter orange, ginkgo, licorice, St. John’s wort, and yohimbine.
Watch the salt in your diet.
When looking at salt, it is important to note the salt you add to your food as well as the sodium content of the food you buy. Sodium is high in canned and processed foods, such as frozen meals. Look for items marked low sodium or rinse your canned foods before eating.
Participate in regular physical activity.
Physical activity strengthens your heart and helps to manage stress. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week. Pick activities you enjoy and ones that make your heartbeat faster, your muscles stronger, and your muscles and joints more flexible.
Quit smoking.
Tobacco is a stimulant, meaning it raises blood pressure. Within two weeks of quitting smoking, your circulation begins to improve, and within 3-6 years after quitting smoking, your risk of heart disease is reduced by 50%.
Eat a well-balanced diet.
Vitamins and minerals from fruits, vegetables, nuts, and fish have known benefits on heart health and blood pressure. Eating a well balanced diet will also help you to maintain a healthy weight.
Monitor your blood pressure at home. 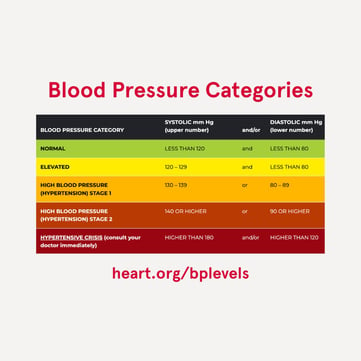
Taking your blood pressure at home will help give you and your health care team insights into how well your medications and lifestyle are maintaining your blood pressure. It is important to keep a log of your blood pressure readings and bring it to your appointments.
Knowing what lifestyle factors contribute to high blood pressure is an important part of managing your high blood pressure. By incorporating healthy habits and avoiding medications that can raise your blood pressure, you can better manage your blood pressure and reduce the chance of long-term risks such as heart attack and stroke.
Talking with your doctor, APP or pharmacist can help you by providing personalized guidance and support. The American Heart Association has many resources for your reference that can help guide those discussions. Your heart health starts with you, and you can make every beat count.